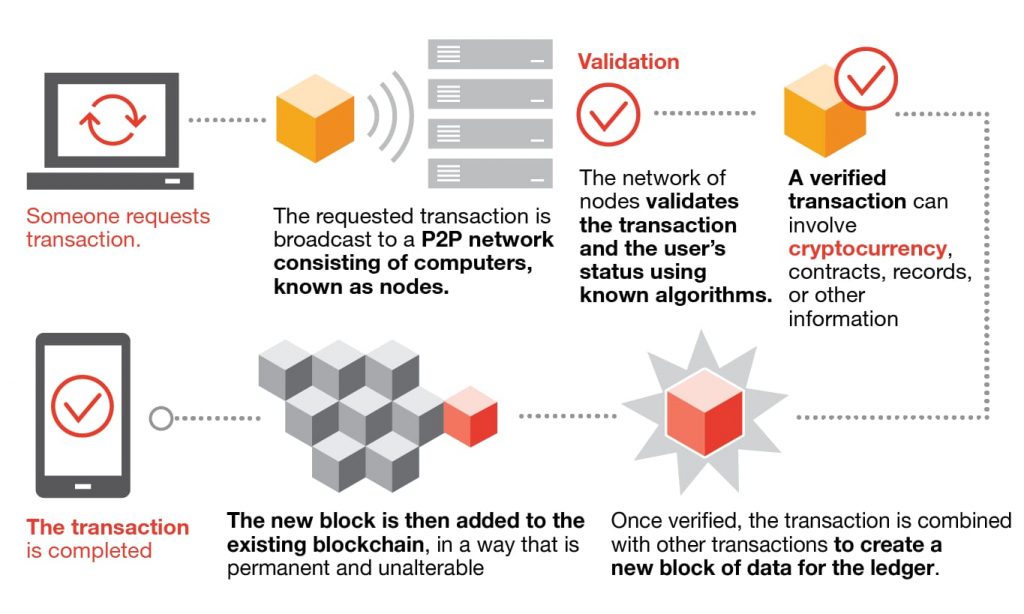
In today’s globalised economy, the role of procurement and supply chain management (PLSCM) has become increasingly critical. Businesses rely on efficient supply chains to maintain competitiveness, reduce costs, and ensure customer satisfaction. As a result, there is a growing demand for professionals who are well-versed in the complexities of supply chain management. Pursuing a master’s degree in PLSCM can provide individuals with the knowledge, skills, and credentials needed to excel in this dynamic field.
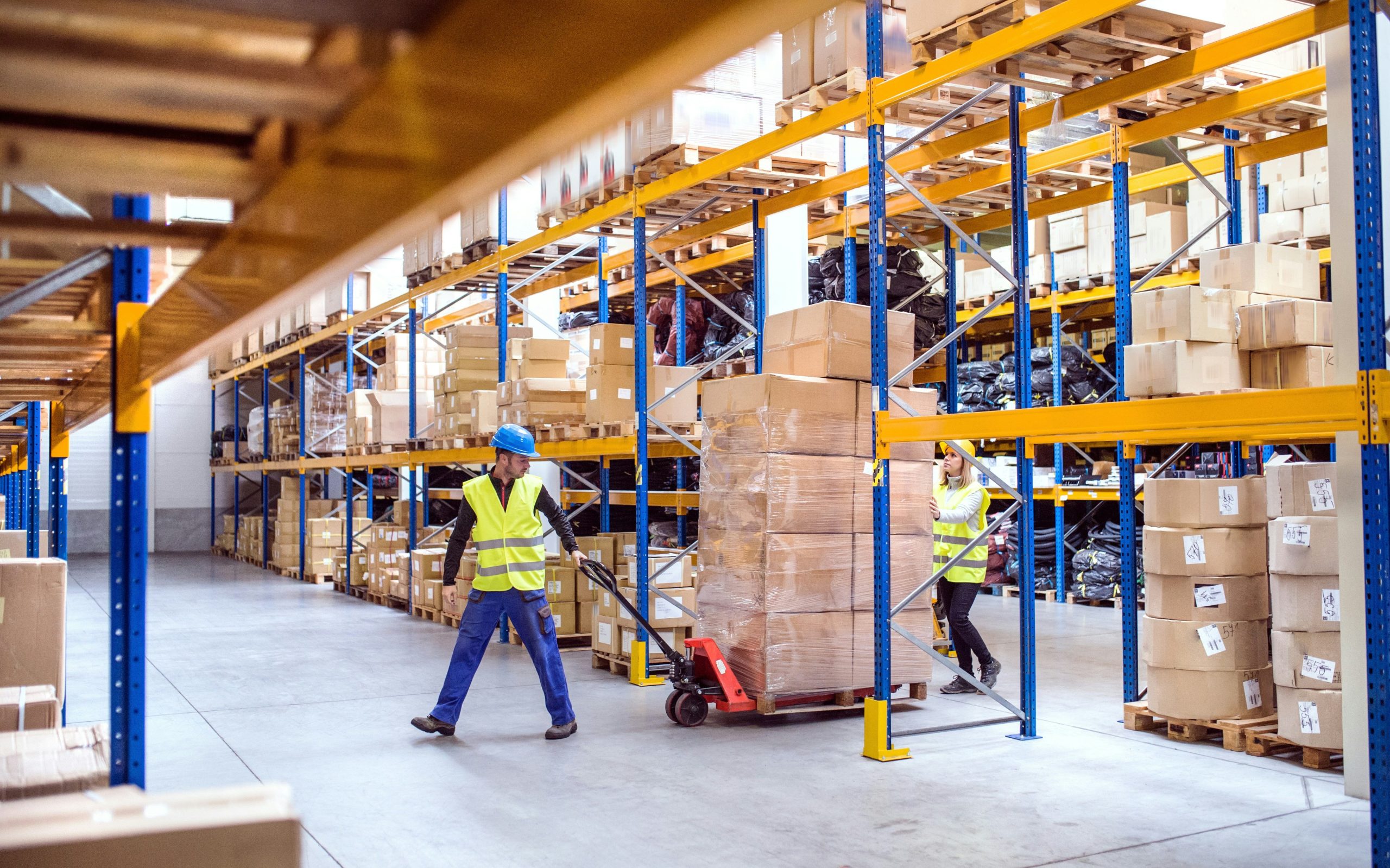

Robert Kennedy College (RKC), in exclusive partnership with the University of Salford, UK, offers a globally recognised online MSc programme in Procurement, Logistics and Supply Chain Management. The programme is also accredited by the Chartered Institute of Purchasing and Supply (CIPS) and the Chartered Institute of Logistics and Transport (CILT).
As we approach the New Year and the holiday season draws near, it is especially important to maintain sufficient stock levels to ensure that all customers, along with their friends and family, enjoy a joyful and hassle-free season.

The festival season is a time of joy, celebration, and increased consumer activity. For businesses, it represents a critical period where demand surges and the ability to meet this demand can significantly impact their success. A robust supply chain is essential to ensure product availability, customer satisfaction, and smooth operations. This becomes even more critical during the holiday season, as businesses must optimise their strategies to thrive in this busy period.
Here are ten reasons why a strong supply chain is vital during the festive season, along with insights on how businesses can enhance their supply chain strategies for success.
(1) Meeting Increased Demand
One of the most significant challenges during these times is the spike in consumer demand as people tend to shop more, both online and offline. A strong supply chain ensures that businesses can keep up with this increased demand without facing stockouts or delays. This involves accurate demand forecasting, efficient inventory management, and timely stock replenishment
(2) Enhancing Customer Satisfaction

Making sure customers are happy during the holidays is vital because it adds to the joy they are already feeling. With so many options available, customers are likely to switch to competitors if they experience delays or stockouts. A well-managed supply chain ensures that products are available when and where customers want them. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also builds brand loyalty, which can have long-term benefits for the business.
(3) Reducing Operational Costs
An efficient supply chain minimises operational costs by optimising processes like procurement, production, and distribution. Even minor inefficiencies can cause substantial cost overruns when volumes are high. Streamlining operations and removing bottlenecks enables businesses to cut costs and enhance their bottom line.
(4) Managing Supplier Relationships
Strong supplier relationships are crucial for a smooth supply chain. During peak demand periods, businesses need to ensure that their suppliers can meet the increased demand and deliver products on time. This requires effective communication, collaboration, and sometimes even strategic partnerships. By collaborating closely with suppliers, businesses can ensure a steady flow of goods and avoid disruptions.
(5) Leveraging Technology
Technology plays a vital role in modern supply chain management. Advanced tools and systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), WMS (Warehouse Management Systems), and TMS (Transportation Management Systems) can help businesses manage their supply chains more effectively. These technologies can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, track shipments, and optimise routes, ensuring that products reach customers quickly and efficiently.
(6) Ensuring Flexibility and Agility
The festival season can be unpredictable, with sudden changes in demand and supply chain disruptions. A strong supply chain is flexible and agile, capable of adapting to these changes quickly. This involves having contingency plans in place, such as alternative suppliers, backup transportation options, and flexible inventory policies. By being prepared for the unexpected, businesses can maintain continuity and avoid disruptions.
(7) Enhancing Collaboration Across the Supply Chain

Collaboration across the supply chain is essential for smooth operations during the festival season. This includes collaboration between different departments within the organization, as well as with external partners such as suppliers, logistics providers, and retailers. Effective collaboration ensures that everyone is on the same page and working towards common goals, leading to better coordination and efficiency.
(8) Focusing on Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in supply chain management. Businesses can leverage their supply chains to promote sustainable practices, such as reducing waste, minimising their carbon footprint, and using eco-friendly packaging. A robust supply chain can help businesses achieve their sustainability goals while also meeting customer expectations for environmentally responsible products.
(9) Utilising Data and Analytics
Data and analytics are powerful tools for optimising supply chain performance. During peak demand periods, businesses can use data to gain insights into customer behaviour, demand patterns, and supply chain performance. This information can be used to make informed decisions, such as adjusting inventory levels, optimising transportation routes, and improving supplier performance. By leveraging data and analytics, businesses can enhance their supply chain efficiency and responsiveness.
If Data Analytics is a field you are looking to specialise in then RKC offers an MSc programme in Data Analytics.
(10) Preparing for Post-Festival Demand
The holiday season does not end with the last day of celebrations. Businesses need to be prepared for the post-festival period, which can also see high demand due to returns, exchanges, and continued shopping. A strong supply chain ensures that businesses can manage this extended period of activity without disruptions. This involves planning for reverse logistics, managing returns efficiently, and maintaining adequate inventory levels.
To conclude, a strong supply chain is the backbone of business success. It ensures seamless operations, meets heightened customer expectations, and minimises disruptions during this peak period. By investing in efficient supply chain strategies, businesses can not only thrive but also gain a competitive edge, fostering long-term customer loyalty and sustainable growth.

If you want to do an online degree programme in another specialisation then explore several specialised master’s/bachelor’s/PhD degree programmes that Robert Kennedy College offers through exclusive partnerships with top British universities. You could also chat live with our team of Education Advisers on WhatsApp, who can have a look at your profile and give you some advice.
If you have already made up your mind, click here to apply.