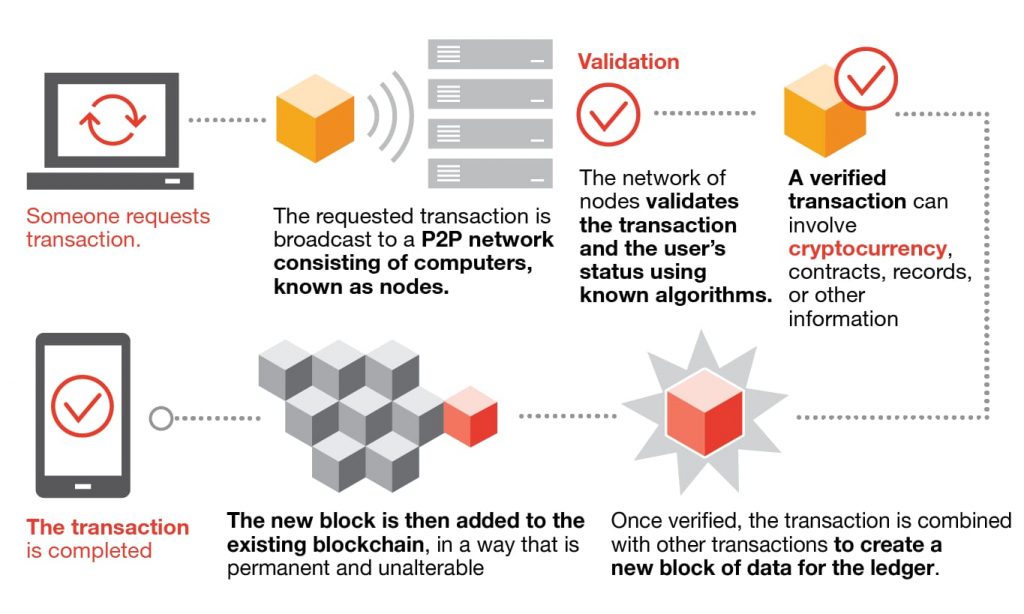
Financial Service Management (FSM) holds a critical role in ensuring the seamless functioning of financial institutions and the effective provision of financial services to clientele. In this blog, we’ll delve into the essence of Financial Service Management, exploring its essential components, associated challenges, and strategies to enhance this vital function.

Grasping the Concept of Financial Service Management
Financial Service Management involves the strategic and operational oversight of financial services within an organization. Its scope encompasses a variety of activities aimed at maximizing financial efficiency, ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines, enhancing customer satisfaction, and ultimately driving business growth.
Key Elements of Financial Service Management
Risk Mitigation: Identifying and addressing risks tied to financial services to maintain stability and long-term sustainability.

Regulatory Compliance Management: Adhering to legal and regulatory frameworks to sustain trust, credibility, and legality within the financial industry.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Implementing strategies to nurture and manage customer relationships, delivering tailored financial solutions to meet their specific needs.
Operational Streamlining: Enhancing internal processes and operations to boost productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall organizational efficiency.
Integration of Technology: Leveraging advanced technologies and systems to optimize operations, bolster security, and deliver innovative financial services.

Hurdles in Financial Service Management
Financial Service Management encounters several challenges, including:
Regulatory Transformations: Adapting to evolving regulations and compliance requirements in diverse regions, often intricate and time-consuming.
Technological Evolution: Staying current with rapidly evolving technologies, including cybersecurity measures, to safeguard sensitive financial data and transactions.

Meeting Customer Demands: Fulfilling diverse customer expectations and preferences, such as personalized services, ease of use, and 24/7 accessibility to financial services.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: Addressing cybersecurity risks and threats to safeguard sensitive financial data from potential breaches and cyberattacks.
Strategies for Effective Financial Service Management
Investing in Technological Advancements: Implement cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics to enhance operational efficiency, customer experience, and security.
Continuous Training and Education: Provide ongoing training to employees to keep them updated with the latest regulations, technologies, and industry best practices.

Customer-Centric Approach: Understanding customer needs and preferences and customizing financial services to effectively address them, fostering long-term customer relationships.
Encouraging Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaborate with industry partners, regulators, and other stakeholders to share insights, best practices, and collectively drive industry growth.
Emphasizing Data Security and Compliance: Prioritize data security and compliance with regulations by implementing robust cybersecurity measures and conducting regular audits.
In summary, Financial Service Management is a multifaceted discipline that necessitates strategic planning, technological innovation, and a strong focus on customer needs and regulatory adherence. By embracing these principles and staying informed about industry advancements, financial institutions can elevate their service offerings, manage risks effectively, and achieve sustainable growth in the dynamic financial landscape.