If you ask me, the brain is the most essential part of the human body. Some of you might disagree with me and say it is the heart, lungs, liver, or left pinky finger that is more important, and you might be right, with valid reasons. The fact is, without the brain, nothing else matters. A body without brain activity is just a shell.
So, taking care of the brain, nurturing, and exercising it is crucial if you need to perform at your best. In my opinion, it is more important to keep your brain at peak efficiency than it is to keep your body in the best of conditioning. And like everything else that is related to your body – what you eat is critical in its development.
The Brain
If you removed all the moisture from your brain, what are you left with? Breaking down your dehydrated brain into its constitutional nutritional content, most of its weight comes from the following:
- Fats, aka lipids
- Proteins and amino acids
- Micronutrients
- Glucose
Of course, the brain is much more than just the sum of its nutritional parts. However, each part has an important role in your development, functioning, mood, and energy. So that sleepy feeling you get after your third helping of biriyani (a delicious Indian rice dish, a definite must-try!) could simply be the effect of food on your brain.
Fats aka lipids
The brain has the second-highest lipid content behind adipose tissue, and brain lipids constitute 50% of the brain dry weight. Omega 3 and omega 6 are the most essential fats in your brain, and, as they are critical in preventing degenerative brain conditions, must be included in your daily diet. Therefore, eating omega-rich foods is necessary for the creation and maintenance of cell membrane. Some examples of omega-rich foods are:
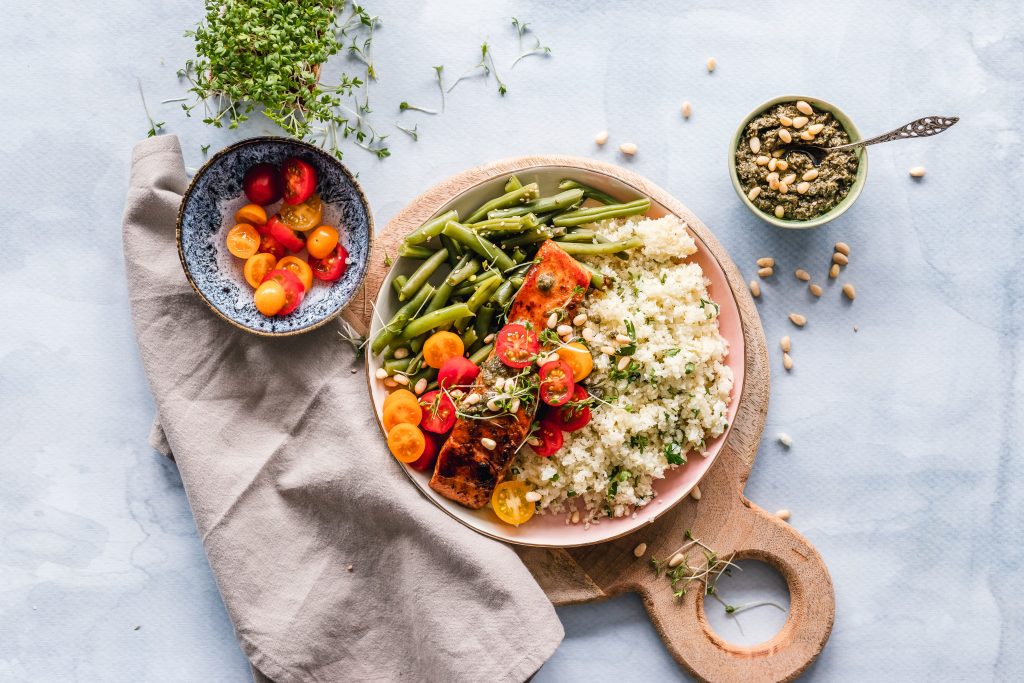

- Fish and other seafood (especially cold-water fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, and sardines)
- Nuts and seeds (such as flaxseed, chia seeds, and walnuts)
- Fortified foods (such as certain brands of eggs, yogurt, juices, milk, soy beverages, and infant formulas)
- Plant oils (such as flaxseed oil, soybean oil, and canola oil)
There are, of course, fats that are bad for your body and brain, like saturated and trans fats, and long-term consumption of these may compromise brain health. So, you know what to look out for, a few examples of “bad fats” are:

- Baked goods, such as cakes, cookies and pies
- Shortening
- Microwave popcorn
- Frozen pizza
- Refrigerated dough, such as biscuits and rolls
- Fried foods, including french fries, doughnuts and fried chicken
- Nondairy coffee creamer
- Stick margarine
I know, that is most of the good things in life. It makes me sad too!
Proteins and amino acids
These are the building blocks of life, of growth, and development. A protein is a chain of amino acids that are connected. They impact how we feel and behave.
Amino acids contain neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that transmit a signal from a neuron across the synapse to a target cell, which can be a different neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell. This has an impact on your sleep patterns, mood, weight, etc.
Different types of foods can have a vastly different impact on how we feel. For example, pasta can give us a feeling of calm, or protein can make us energised. This is why having a balanced diet is essential because you don’t want to swing your mood around too much.
Micronutrients
According to the World Health Organization – micronutrients are vitamins and minerals needed by the body in very small amounts. However, their impact on a body’s health is critical, and deficiency in any of them can cause severe and even life-threatening conditions. They perform a range of functions, including enabling the body to produce enzymes, hormones, and other substances needed for normal growth and development. Micronutrient deficiencies can cause visible and dangerous health conditions, but they can also lead to less clinically notable reductions in energy level, mental clarity, and overall mental capacity. This can reduce educational outcomes, reduce worker productivity, and increase risk from other diseases and health conditions.
Five micronutrients — vitamin B6, vitamin C, vitamin E, magnesium, and zinc — play roles in maintaining the immune function. The following are a few examples of micronutrient rich foods:

- Vitamin B6 – Chicken, cereals, bananas, pork loin, potatoes with skin
- Vitamin C – Tomatoes, citrus fruit, sweet peppers, broccoli, kiwi fruit
- Vitamin E – Sunflower seeds and oil, almonds, safflower oil, peanut butter
- Magnesium – Whole wheat, legumes, nuts, seeds
- Zinc – Oysters, beef shank, Alaskan king crab, turkey (dark meat)
Glucose
The human brain only makes up about 2% of our body weight, yet it uses up to 20% of our energy resources. Most of this energy comes from carbohydrates that our body digests to glucose. The brain, specifically the frontal lobe, is so sensitive to drops in glucose levels that a physical change in mental functions becomes visible.
According to an article by the Harvard Medical School (HMS), brain functions such as thinking, memory, and learning are closely linked to glucose levels and how efficiently the brain uses this fuel source. If there isn’t enough glucose in the brain, for example, neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers, are not produced, and communication between neurons breaks down. In addition, hypoglycemia, a common complication of diabetes caused by low glucose levels in the blood, can lead to loss of energy for brain function and is linked to poor attention and cognitive function.
The brain is dependent on sugar as its main fuel; it cannot be without it.
Vera Novak, MD, PhD, an HMS associate professor of neurology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Assuming we have carbs on a regular basis, the type of carbohydrates we eat can also have a varied impact on the brain. For example, high glycaemic foods, such as white bread, cause a rapid release of glucose into the blood, followed almost immediately by a quick dip in blood sugar. This results in shortened attention span and mood swings. On the other hand, foods like oats, grains, and legumes release glucose gradually, resulting in a more sustained level of attentiveness.

Again, a balanced intake of carbohydrates is needed to get your brain performing at peak efficiency.
So, there are tangible benefits to following a diet plan. However, do not go about changing your diet on your own; you never know the impact your diet can have on your body and health. Instead, consult your doctor, a nutritionist, or both, tell them your goals and work with them to develop a dietary plan.
We would like to hear from you – please comment below on the impact following a diet has had on you. How were you able to stick to your diet?
While our Education Advisors (EA) are no nutritionists, you can always chat LIVE on WhatsApp with one of our Education Advisors for more information on all the 100% online master’s degree programmes we offer and the application process.
