The first time I heard the phrase “The Internet of Things (IoT)” (and that was not too long ago), my reaction was – “Wooohhaat the hell is that?! Speak English man!”
Now, my understanding of IoT is still very limited, and when I decided to write a blog on one of the new programmes we at Robert Kennedy College (RKC) launched through our exclusive partnership with the University of Cumbria (UoC), UK – 100% Online MSc Computer Science and International Business, I was happy to find that one of the modules in the programme was IoT.
Now, what can one actually write about a management programme in Computer Science and International Business? I certainly couldn’t think of anything, apart from information about the programme, which can anyway be found on our website. So, I decided to get a better understanding of IoT and pass it on to all those in the same boat as I, or who may be looking to do this programme with us.
What is the Internet of Things?
We live in a digital world and have reached a point where most anything in the digital space can basically talk to other “things” digital and share data – we can share data through networking between our communication devices, between multiple and different apps and software. But until quite recently, this sharing was not possible in the physical world.

But now, technology has advanced to the point where we are able to build a network of multiple physical objects, connect it to the internet, to send, receive, and interpret data. And this is the Internet of Things.
I know it sounds complicated, but nowadays, we actually see it in a number of places and don’t actually realise it, taking it for granted. I saw it work at the end of last year and was impressed but did not know what I was looking at.
My family and I were on holiday in Abu Dhabi and were lucky enough to be staying at W Hotel, Yas Island, and got an upgrade to a suite. The entire room was connected. As an example, every item in the minibar was detected and listed as removed on a screen. Housekeeping restocked as soon as we were out of the room and it was billed automatically.
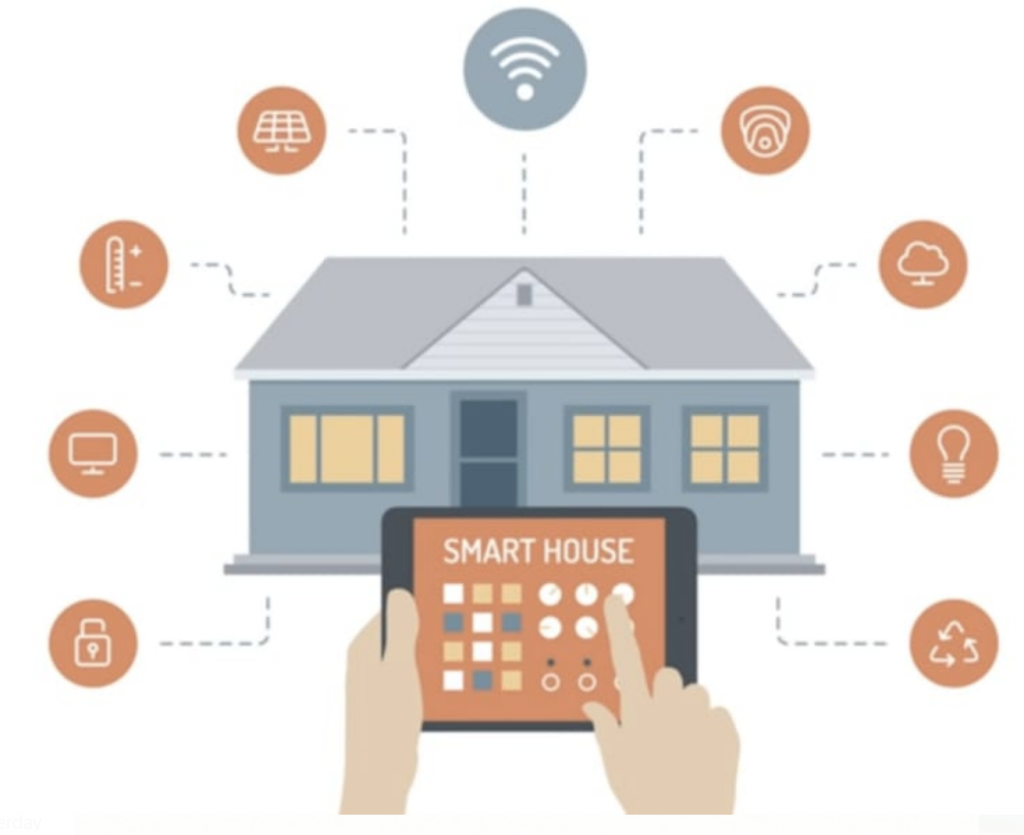
People who use Google Home, Apple Homekit, Amazon Alexa, or Philips Hue are already familiar with the technology.
How does IoT actually work?
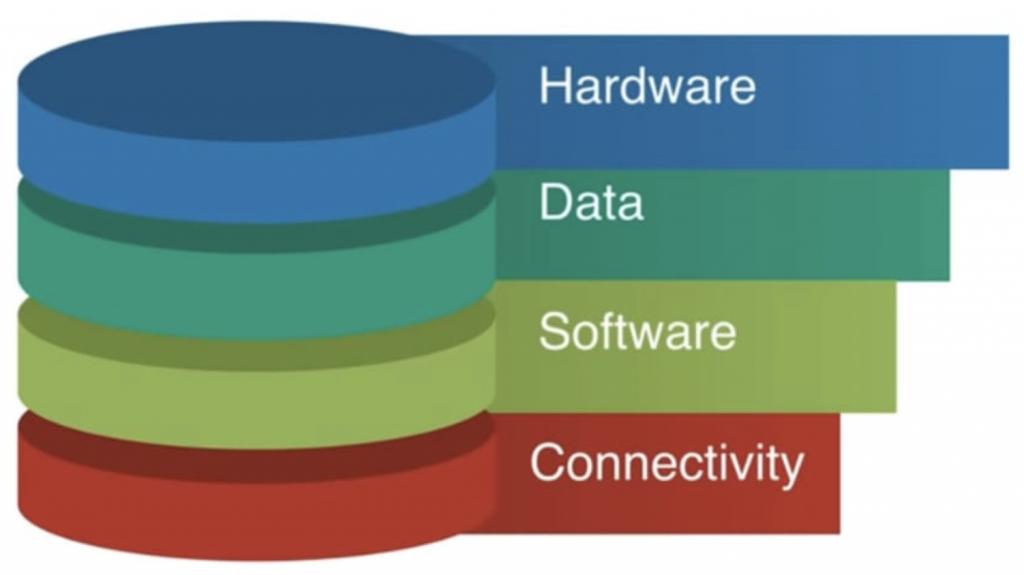
The working of IoT can basically be broken down into four sections:
- Hardware – is what helps us connect digital items to physical objects. The hardware is what senses things and converts that to data.
- Data – is the information that the hardware collects. It is what will help us make sense of how everything is working, becoming the true universal language, the universal language of “things”.
- Software – is what interprets all the information and enables the use of information. Software is what takes data from the hardware and extracts value for the end user.
- Connectivity – without connectivity there is no IoT. 2g, 4g, 5g, wi-fi, Bluetooth, without connectivity there is no exchange of data and IoT would have only remained a concept that some genius penned down.
Is IoT practical?
The simple answer is – YES! This is not science fiction; it is already is daily use. It is cheap and easy to build – the hardware can be bought out of the box, the software is readily available (that is, for those of us too lazy or who don’t have the knowledge to make or create it on our own, but are good at marketing and selling). And finally, they are simple and easy to use, especially if you make it compatible with Google, Apple and Amazon. And because of cloud computing and networking, IoT can be done from anywhere, at a low cost, with minimal maintenance.

In fact, most of us already use IoT today, from turning on our Philips Hue lights to a colour and brightness matching our mood, to automatically switching on or off our air conditioner and heating systems, to security systems that monitor our homes and alert us when there is an unauthorised entry. All this is done live, from the tips of our fingers, with your preferences backed up on the cloud and available across all systems.

The impact of IoT on industry
According to a McKinsey & Company report in 2017, the impact of IoT across industry will be approximately US$11 Trillion annually by the year 2025.
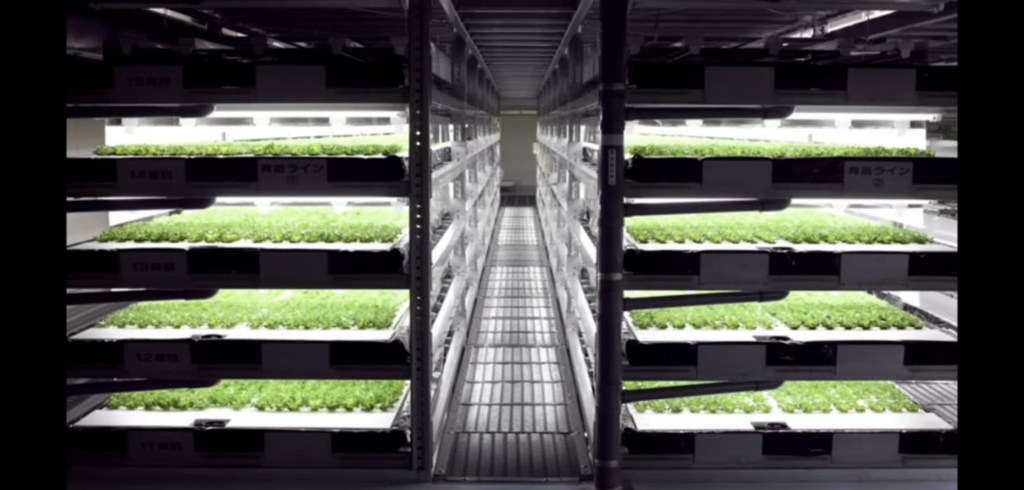
The impact on industry is already telling, especially in terms of cost savings. As an example, vertical farms, where the only human interaction needed is at the time of planting. Watering, trimming, and harvesting are all taken care of by IoT systems.

Another good example of IoT integration to reduce costs and increase profitability is the city of Barcelona, which was one of the first European cities to adapt smart city technologies. Simple implementation of parking sensors informing motorists of where parking spaces are available has increased the revenue generated from parking to over US$50 million per year. By having IoT systems in public lighting has enabled Barcelona city to reduce their energy costs by over US$37 million per year. And finally, their smart gardens have saved them US$58 million a year by just efficient water usage.
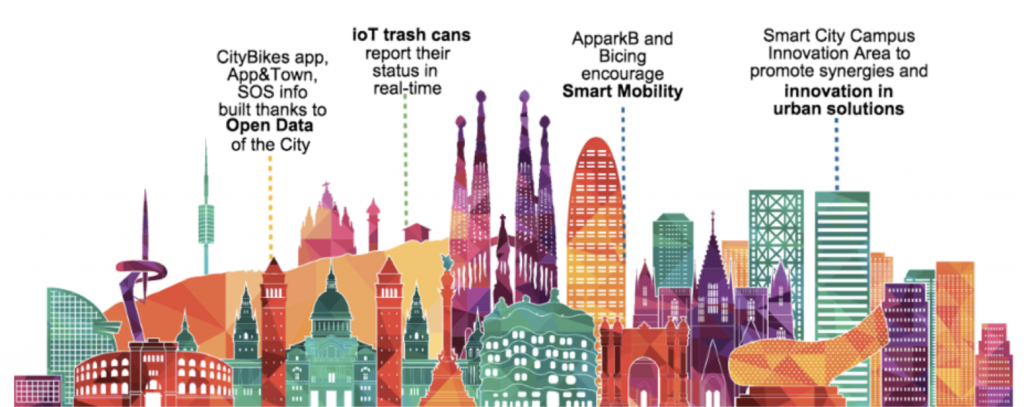
And as technology is always changing, the city of Barcelona has also incorporated these changes to have a direct and positive impact on the lives of its residents. The use of smart phones has enabled residents to receive instant alerts and updates from the city about employment, housing, administration, mobility, health services, security and utilities.
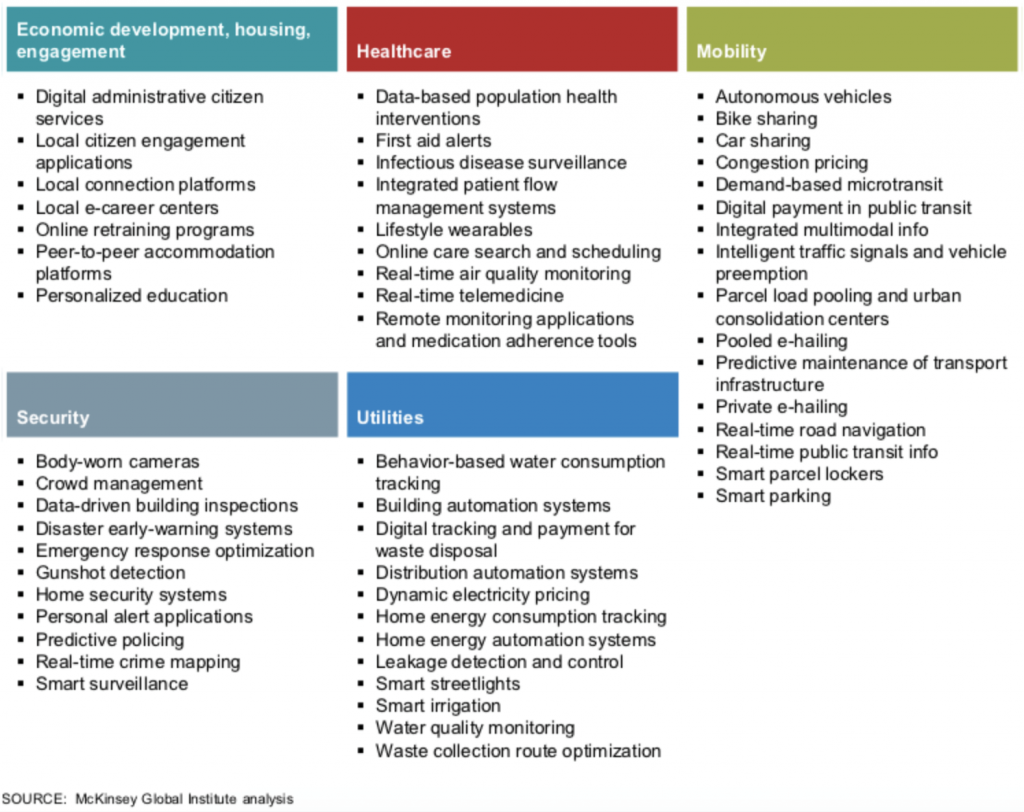
A recent study (2018) of McKinsey: Smart Cities: Digital solutions for a more livable future distinguished 55 applications within the fields shown below. According to this study, these applications are capable to improve quality of live by 10 – 30%.
Now for the cons of IoT
The “force” cannot exist without the “dark side” (Star Wars reference), and now that we have ranted and raved about how wonderful IoT is, here are a couple of its more obvious drawbacks.
The biggest and most obvious disadvantage of IoT is data security and privacy. As mentioned earlier, creating an IoT device is not too difficult or expensive to make, and in their rush to become the first mover and trendsetter, most manufacturers tend to overlook the security aspect of IoT. Keep in mind, in most cases, you will have to enter your personal information, and in some cases, even your credit card information to effectively use your IoT enable devices. Now, these devices usually work in a network and are on the cloud, so if there isn’t firewalls and security, your privacy and data can be at risk.
Another unexpected drawback, if you can even consider it that, as it is caused due to the increase in efficiency due to implementation of IoT, is to increase in the short-term unemployment. With the increase in efficiency, the workforce required to do a particular job will be streamlined. While this has the positive impact of reducing costs and the turnaround time to job completion, it also has the unintended consequences of leaving a large percentage of the workforce either unemployed or having to be retrained in a new job skill.
A good example of the massive impact IoT is having on the retail industry is Amazon Go. The evolution of how everything from merchandising and stocking, supply chain management, human resources, and billing, in the retail industry is just amazing to see.
Finally, the importance and potential future impact of IoT cannot be understated, especially in the era of social distancing. The judicious and responsible implementation of IoT will free up humanity to do what we do best – create, innovate, learn, socialise and moving on to the next “big thing”. Which is why IoT, as a study module, is integral to a number of programmes offered by Robert Kennedy College.

You can also chat LIVE on WhatsApp with one of our Education Advisors for more information on the programmes offered, application process, and for more information on any discounts we might be running in this rather strange period of our lives.
